I first ‘met’ Harriet Edquist when presenting at Wheels Across the Pacific: Transnational Histories of the Automobile Industry, a virtual conference organized jointly by the AHA [Automotive Historians Australia] and the SAH [Society of Automotive Historians]. The objective of the symposium was to explore ways in which the Australian and North American auto industries shared parts and components, staff, expertise and skills, engineering, design and studio practices, business and management structures, and advertising and trade practices. Dr. Edquist, a professor of architectural history at RMIT [Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology] and Director of RMIT Design Archives, was both an organizer and presenter. She was also, as it turns out, an integral presence in my own paper, which focused on women’s automotive history scholarship in both the United States and Australia. As I noted in my presentation, automotive history has been slow to incorporate the influences and practices of women. It wasn’t until the later part of the twentieth century that women’s absence from the automotive archives was noticed and addressed. Feminist scholars in Britain, the US, and Australia took upon the arduous and important task of writing women into automotive history. Edquist is one of the more recent contributors to this critical chronicle of women and the automobile.
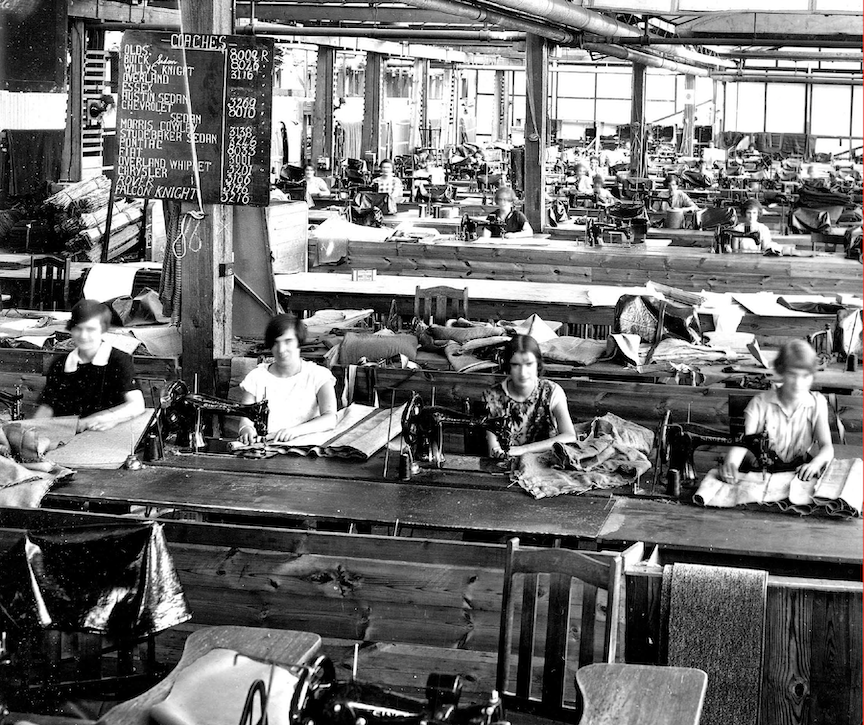

Although Edquist’s research projects focus primarily on architectural and design history, her automotive interests have broadened the scope of her scholarship to include automotive design and women’s participation in the Australian auto industry. Through her investigation of women’s automotive experience in the early decades of the twentieth century – women as drivers and mechanics; their opportunities as production workers; and as designers and engineers – Edquist has effectively built on the research of fellow Australians Kimberley Webber and Georgine Clarsen to bring attention to the various ways women have engaged with the automobile over time. “In Women in the Early Australian Automotive Industry: A Survey“, co-authored with Judith Glover, Edquist calls upon variety of sources – photographs, newspaper articles, mail correspondence, RACV archives, online resources, automotive forums, journal articles, dissertations, and automotive design archives and publications – to recover Australian women from automotive obscurity and bring attention to how they experienced automobility as workers and drivers.
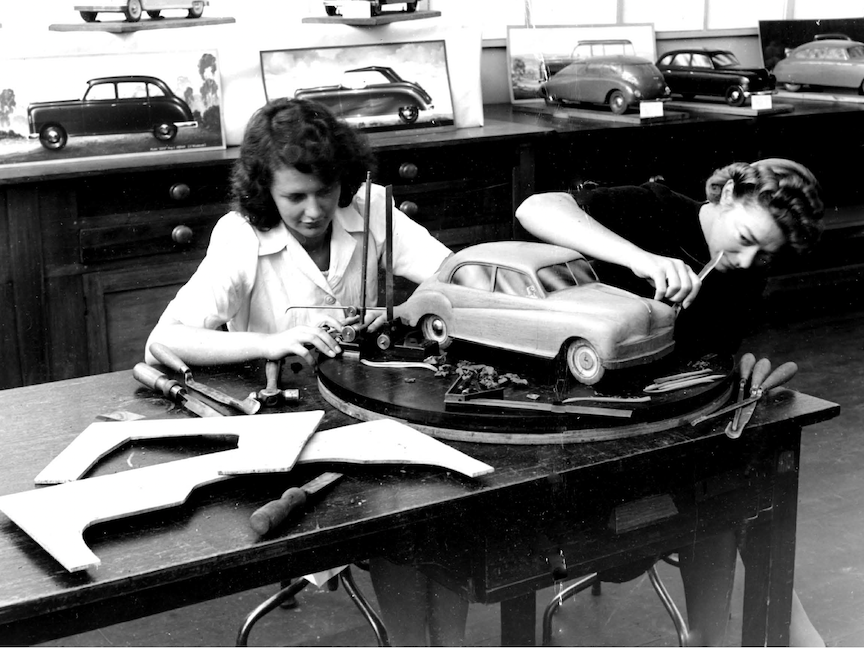

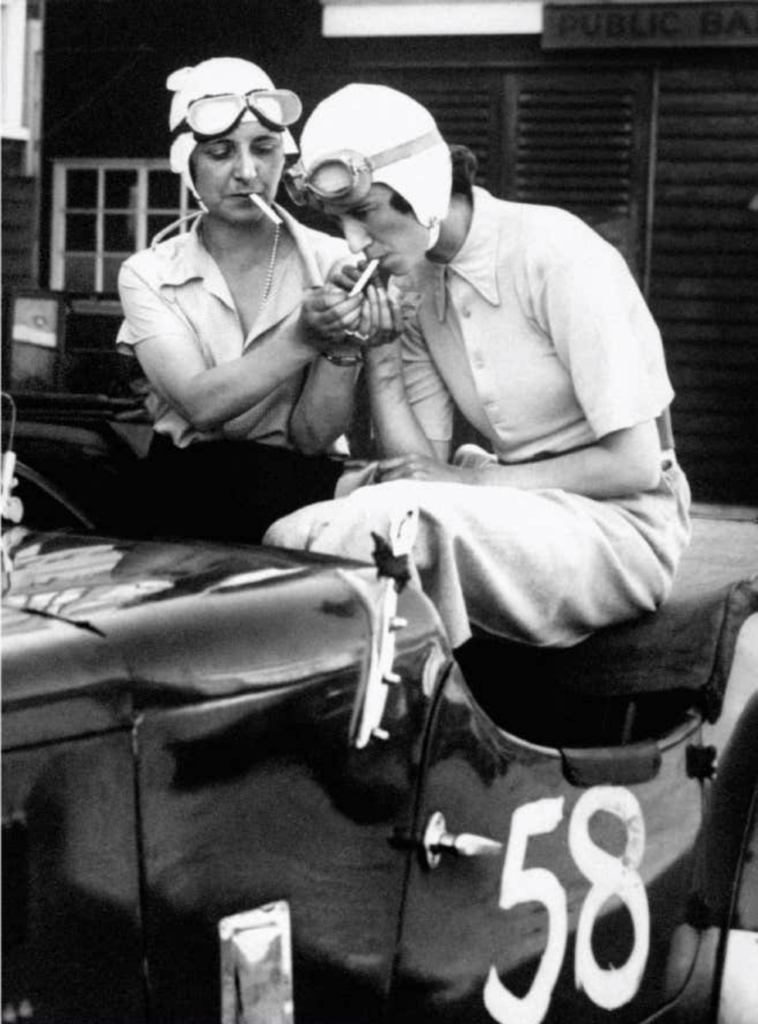
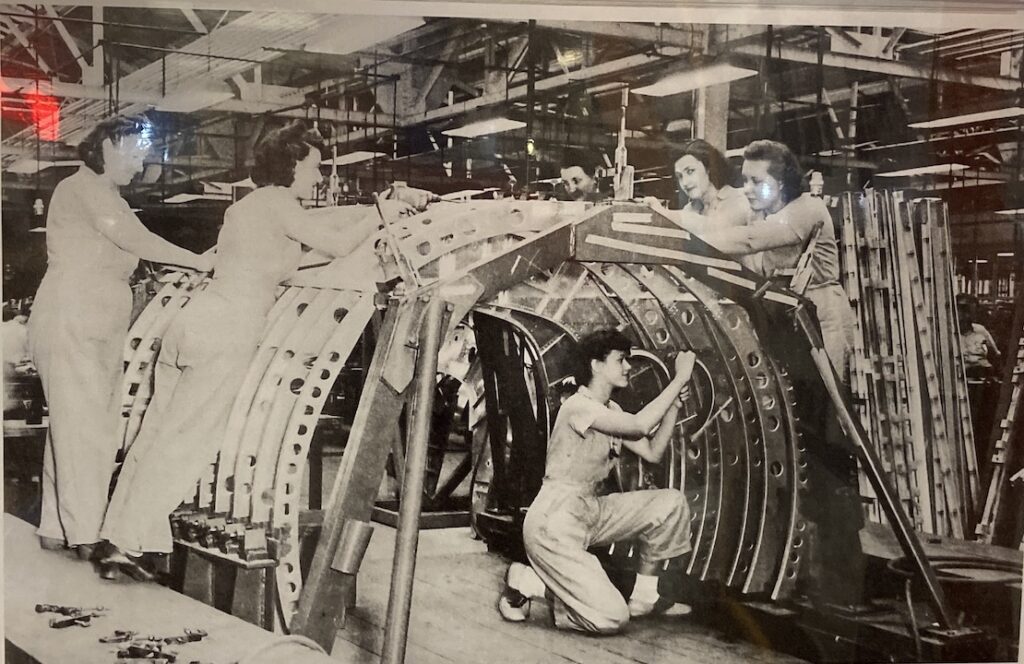
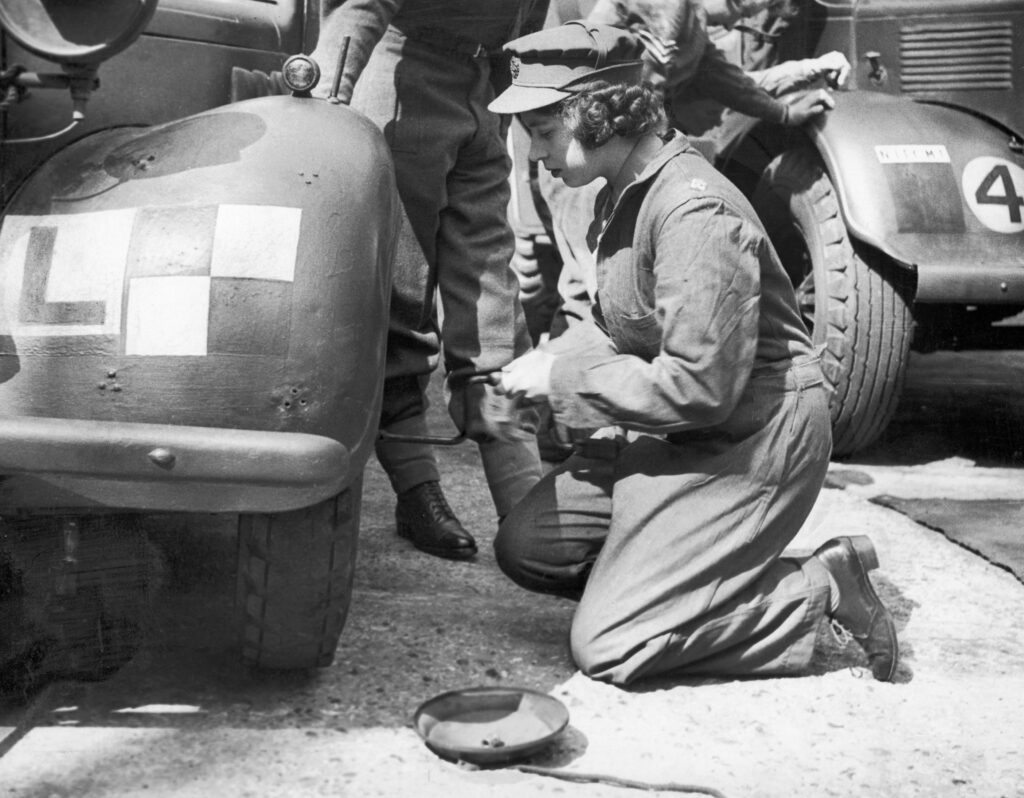
In this engrossing essay, Edquist and Glover examine women’s efforts to become recognized as legitimate drivers through long distance auto tours and participation in the growing sport of auto racing. Both automotive activities provided opportunities for women to gain proficiency not only behind the wheel, but under the hood as well. The authors cite Clarsen’s argument that the media’s fascination with female drivers ‘criss-crossing’ the continent was an important component of nation-building as well as a means to present Australia as modern and civilized. This was particularly interesting to me as an American, as women’s long distance tours in the US during this time served primarily as marketing tools for various auto manufacturers. Edquist and Glover also call upon case histories and recovered photographs to illustrate women’s participation in the car industry as production workers as well as automotive engineers and designers.
The recent work of Edquist and Glover presents new evidence of Australian women’s engagement with cars as drivers, workers, and designers. Important in its own right, the study also suggests the possibilities of further research into women’s automotive history and hopefully prompts additional investigative projects in both Australia and the United States.